Updating WordPress
WordPress can bring such reliability to your website that you may easily forget that it is an actively maintained platform and is in constant development. WordPress releases regular updates to its software, including security patches, and even provides the tools to quickly and easily update your site to the most recent version.
Sometimes, the changes to WordPress will contain major functionality changes and even new features. When this happens, it will be referred to as an upgrade. This will usually happen once a year, though sometimes it may be less frequent.
This article will address the following topics:
- Should I update WordPress? ⤵
- What problems can upgrading cause? ⤵
- What should I do before updating? ⤵
- Okay, I'm ready. how do I update WordPress? ⤵
- What if something goes wrong? ⤵
Should I update WordPress?
Yes. You may be skeptical of this answer as it is simple and straightforward. It is exceedingly rare to provide such a ubiquitous answer for such complicated issues. However, in this case, the answer is simply and unequivocally yes.
Reasons why you always need to update WordPress
Security
There is an active community of developers constantly improving and building WordPress to combat active, intelligent, and capable communities of hackers looking for vulnerabilities.
Hackers will find and expose flaws in logic and programming, eventually allowing malicious users to access older WordPress versions. This is every bit as bad as it sounds. It sometimes gives direct access to your hosting account and its files, possibly allowing them to serve malware to your visitors.
Widespread adoption of the WordPress platform means a high return on investment for hackers who find vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities become well documented and exploitable for everyone using the compromised version of WordPress.
After reading this, and if you did not already know this before, you might feel worried. It can be daunting to suddenly realize that there is an active community of hackers constantly working to find vulnerabilities in your software and publishing those vulnerabilities online for everyone to see. But there is good news.
The good news is that the WordPress community is devoted to closing these vulnerabilities, updating their software constantly. This community pays careful attention to documented vulnerabilities and releases patches as frequently as possible to close them and ensure that sites are as secure as possible, but there is a catch.
The catch is that you have to update your WordPress as often as a new update is available. Even if there were no other reasons to update your WordPress, this alone is reason enough to do so.
Optimization
Updates to the WordPress code frequently include improvements to the CPU usage of your site. Optimization is important because it functionally determines how many people can visit your website at once.
A well-optimized site can serve a very large user base even on shared hosting, and it can help your site load faster and more efficiently for all of your users. Site administrators who care about their Google ranking should care about how fast your site loads, as Google considers when indexing your site.
Other users may rely on a well-developed site to ensure that their hosting costs remain affordable. Being able to deliver a website to visitors quickly and efficiently can determine the type of hosting you can use. A site that uses a large number of resources cannot function on shared hosting due to its effect on the server.
Over time WordPress has consistently improved the platform's optimization, but to take advantage of that optimization, you have to update your site.
Features
WordPress is constantly adding new features. To use them, though, you have to update your site. These can include connectivity and the ability to use logins across websites, new image serving tools, etc.
Every new release is better than the last, and the difference can be night and day between WordPress releases.
Compatibility
Just like those who actively develop WordPress itself, there is an active community of theme and plugin developers working to provide tools to let you make the best website to meet your needs.
A large portion of this community also provides regular updates to ensure that their themes and plugins are secure and well optimized to take advantage of the best of what is available. While many of these developers try to ensure their plugins still work in older versions of WordPress, this is a low priority for them, given the lack of security and reduced stability.
It is in your best interest to ensure that your site is always up to date, For the most reliable compatibility.
What problems can upgrading cause?
It is important to know that quite a lot can go wrong when you update your WordPress. Plugins or themes that the developers do not actively maintain could potentially cause errors that prevent your WordPress site from loading.
Caching services, plugins, or even your browser may store data from your website prior to the update that may do anything from causing visual issues with your theme to preventing your site from displaying information or even loading.
Fortunately, there are some common troubleshooting steps that will help a vast majority of users easily identify the source of their issue so that they can fix it and proceed with the update. For assistance with this, please see below ⤵.
A small group of users may find that a theme or plugin that is essential to their site is incompatible with the upgrade. These users may ask if they should still upgrade their site given the expense and difficulty of working around core utilities not working.
The answer is still unequivocally yes, though it may require some development to do so correctly.
If components to your site do not function, first restore your site from a backup. Then we recommend taking steps to find replacements for these components so that you may update as fast as possible.
Click below to expand more information on why you should not use an outdated version of WordPress for compatibility reasons.
Why not just keep using an old WordPress version for compatibility?
Your site represents an investment, and HostGator understands how important that investment is to you. Even with that value in mind, the unfortunate reality is that if an aspect of that investment is not compatible with current updates, then it is only a matter of time before it is gone.
These outdated components that prevent you from upgrading to a modern version functionally ensure that your site remains vulnerable to well-documented exploits. This can and will make your site accessible to wide-scale malicious attacks that use calculated patterns to attack every possible outdated WordPress site.
Not taking the time and/or expense to make changes that allow you to keep your WordPress up to date means that when your site can be taken down in ways that you will not be prepared for:
- Google may place malware warning block pages on your site.
- Your host may suspend your site for serving malware to protect their reputation.
- Malicious users may simply delete and replace your site.
If any of these happens, you will experience downtime until you develop a secured site at best. At worst, you may end up serving malware to your users and having users actively recommended not to visit your website until you resolve issues with Google.
You will better serve yourself and your visitors by considering the existing site already obsolete and putting in the effort and expense to make the site up to date rather than waiting to be forced to update while experiencing outages and downtime.
What should I do before updating?
Hey, this is important!
As with any other change to your site, HostGator strongly recommends creating a backup of your site, which you can restore if anything goes wrong. The following article will walk you through making a full cPanel backup:
If you wish to be ready at all times by using automated backups that regularly save revisions of your site that you can restore at the click of a button and alerts you if sketchy changes on your site were found, check out the CodeGuard service:
After creating a backup of your site, go ahead and perform the update knowing that if anything goes wrong, you'll be able to restore from your backup as an option.
Another way of creating a backup is through Softaculous. If you installed your WordPress using Softaculous in your cPanel, you can easily create a backup within the Softaculous dashboard. You can do a restoration of your website via Softaculous using that backup. Please check out these articles for more information.
- How to Create a Backup of Installation With Softaculous
- How to Restore a Backup with Softaculous
- How to Backup A WordPress Site Without A Plugin
Remember, a complete WordPress backup includes the following:
- Your images and media uploads
- WordPress plugins and themes
- WordPress core files
- Of course, your WordPress database!
Okay, I'm ready. How do I update WordPress?
Let's do this!
After ensuring that you are ready to update WordPress, there are 3 methods by which WordPress can be updated:
Here is a video tutorial to walk you through updating WordPress.
Automatic background updates
In an effort to promote better security on the internet and improved site management practices, automatic updates are enabled by default. For WordPress 3.7 and higher, your site should be able to update from 3.7 to 3.7.1, 3.7.2, etc.
For security purposes, HostGator runs a script on our servers that automate updates that cannot be disabled completely. However, you may mitigate the automatic updates by disabling the ones performed specifically by your WordPress installation.
It is strongly advised that you do not disable these automatic security updates. However, if you need to delay automatic updates, please see the information below for instructions on how:
As with all major changes, please create a backup of your website before proceeding. To disable automatic background updates:
- Access the document root of your website using FTP.
- Download the wp-config.php file.
- Edit the wp-config.php with a text editor to add the following line:
define( 'AUTOMATIC_UPDATER_DISABLED', true );
- Save your changes and re-upload the file to your site, overwriting the previous file.
WordPress updates will no longer be automatically installed.
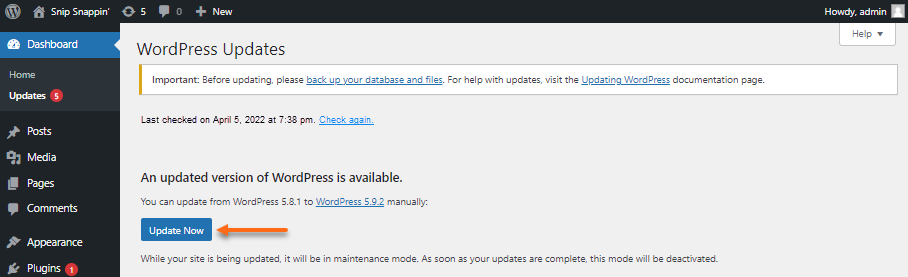
One-click update
Modern versions of WordPress let you update with just one click from the updates menu:
- On the WordPress Dashboard, you will notice that the latest WordPress version is displayed.
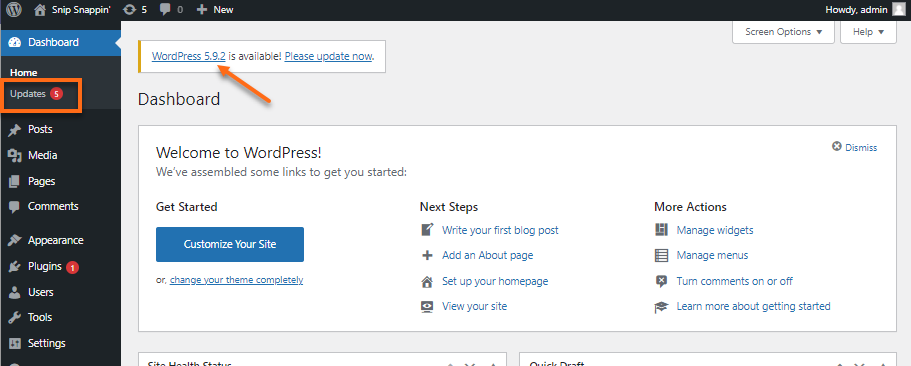
- Select Updates from the left-hand menu.
- At the top of the WordPress Updates section, you will notice the following sections:
- A reminder to back up your site before making an update is displayed.

- The Update Now button will update the WordPress version.
- The Update Plugin section to update your plugins to the latest version.
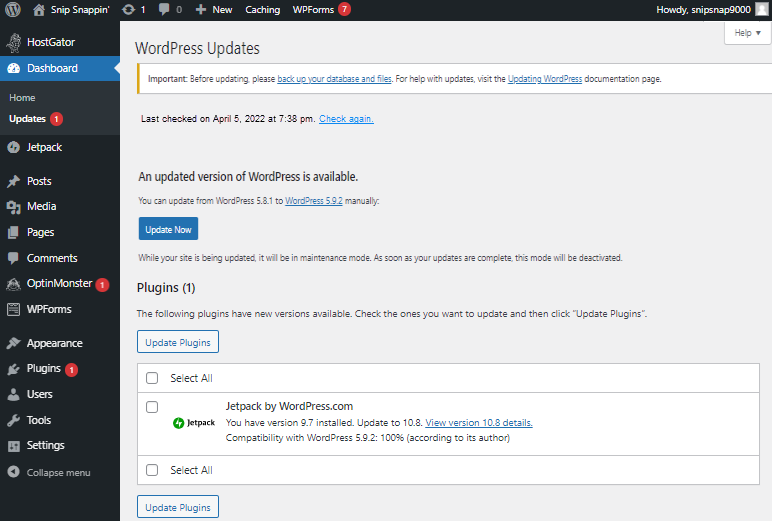
Select the plugin you want to update (or simply Select All), then click Update Plugins to update your plugin(s) version.
- The Update Themes will update your themes to the latest version.
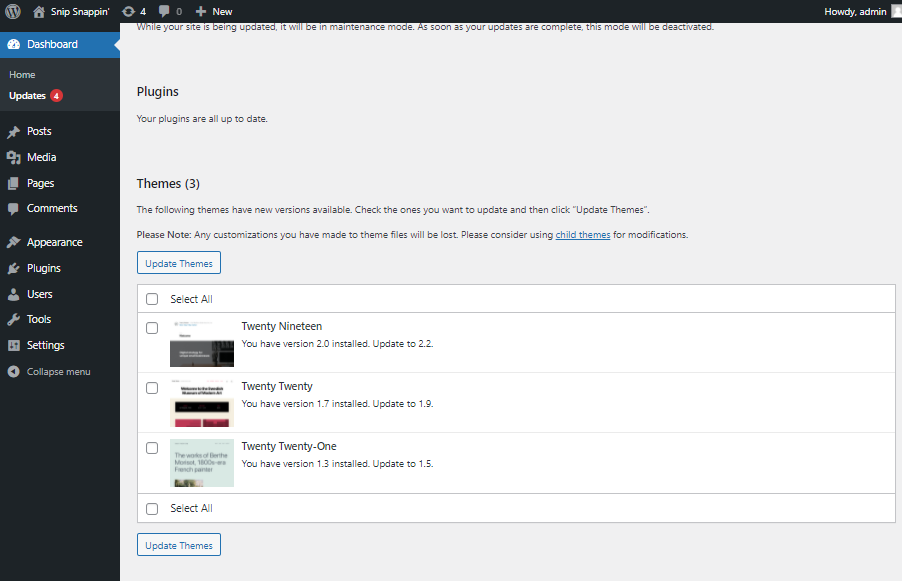
Select the theme you want to update (or simply Select All), then click Update Themes to update your theme(s) version.
- A reminder to back up your site before making an update is displayed.
- Click Update Now to proceed with the WordPress version update.
Manual update
Please see the instructions below for how to manually install WordPress updates:
How to manually update WordPress
While it is a much more involved process that can be difficult to do, you may need to perform a manual update of WordPress if you experience issues with the methods above or after updating.
To manually update your WordPress site:
- It must be emphasized that more than any other upgrade method, because this one is done manually, please create a backup of your site before proceeding.
- Deactivate ALL of your plugins either via WordPress Dashboard or WordPress Command Line Interface
- Download the most up-to-date WordPress version from WordPress.org and extract the files (Do not upload these to your server yet).
- Delete all of your WordPress files EXCEPT for the following:
DO NOT DELETE these files and folders:
- wp-config.php file
- wp-content folder
- wp-images folder (only older installations from 1.5.x days will have this folder)
- wp-includes/languages/ folder: if you are using a language file, and it is here rather than in wp-content/languages/, do not delete this folder (you might want to move your language files to wp-content/languages/ for easier upgrading in the future)
- .htaccess file: if you have added custom rules to your .htaccess, do not delete it
- Custom Content and/or Plugins: if you have any images or other custom content or Plugins inside the wp-content folder, do NOT delete them
Ensure that you DO delete these files and folders:
- wp-* (except for those above), readme.html, wp.php, xmlrpc.php, and license.txt files: Typically files in your root or WordPress folder. Again, don't delete the wp-config.php file. Note: some files such as wp.php may not exist in later versions such as 2.7.
- wp-admin folder
- wp-includes folder: If you have a language file here, remember not to delete the wp-includes/languages/ folder
- wp-content/cache folder: You only see this folder if you are upgrading FROM WordPress 2.0
- wp-content/plugins/widgets folder: You only see this folder if you previously installed the Sidebar Widgets plugin. The Sidebar Widgets code conflicts with the built-in widget ability.
Either cPanel File Manager or FTP may be used to delete these files.
- Use FTP to upload the new files you extracted previously to your WordPress directory.
Note: If you did not delete the wp-content folder, you would need to overwrite some files during the upload.
- Run the WordPress update program by adding /upgrade.php to your dashboard URL. Example:
http://mydomain.com/wp-admin/upgrade.php - Use the instructions in the following article to reset your permalinks:
- From the WordPress dashboard, click Updates from the left-hand menu, and update all of your plugins and themes.
- If you don't find definitions for AUTH_KEY, SECURE_AUTH_KEY, LOGGED_IN_KEY, and NONCE_KEY in your wp-config.php file, you will need to edit that file to add the following security keys.
Modern WordPress installs include 4 security keys, AUTH_KEY, SECURE_AUTH_KEY, LOGGED_IN_KEY, and NONCE_KEY. When each key was added, corresponding salts were added: AUTH_SALT, SECURE_AUTH_SALT, LOGGED_IN_SALT, and NONCE_SALT.
You don't have to remember the keys; use the online generator to create the values for them. You can change these at any point in time to invalidate all existing cookies. This does mean that all users will have to log in again.
Example (don't use these! Generate unique keys.):
Example wp_config.php Codedefine( 'AUTH_KEY', 't`DK%X:>xy|e-Z(BXb/f(Ur`8#~UzUQG-^_Cs_GHs5U-&Wb?pgn^p8(2@}IcnCa|' ); define( 'SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'D&ovlU#|CvJ##uNq}bel+^MFtT&.b9{UvR]g%ixsXhGlRJ7q!h}XWdEC[BOKXssj' ); define( 'LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'MGKi8Br(&{H*~&0s;{k0 define( 'NONCE_KEY', 'FIsAsXJKL5ZlQo)iD-pt??eUbdc{_Cn define( 'AUTH_SALT', '7T-!^i!0,w)L#JK@pc2{8XE[DenYI^BVf{L:jvF,hf}zBf883td6D;Vcy8,S)-&G' ); define( 'SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'I6`V|mDZq21-J|ihb u^q0F }F_NUcy`l,=obGtq*p#Ybe4a31R,r=|n#=]@]c #' ); define( 'LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'w(hdXW|0M=X={we6;Mpvtg+V.o define( 'NONCE_SALT', 'a|#h{c5|P &xWs4IZ20c2&%4!c(/uG}W:mAvyA secret key is a password with elements that make it harder to generate enough options to break through your security barriers. A password like "password" or "test" is simple and easily broken. A random, unpredictable password takes years to break. A Salt is used to further enhance the security of the generated result.
The four keys are required for enhanced security. The four salts are recommended. WordPress will generate salts for you if none are provided.
- Reactivate the plugins and theme you wish to use
Your manual upgrade of WordPress should now be complete. If any issues occur, you may wish to restore from the backup you made in step one and try again or seek assistance with making this change.
What if something goes wrong?
Don't panic!
The first thing to remember when something after an update is Don't Panic! The vast majority of issues with updates can be resolved with some simple troubleshooting. Remember to always try the following steps first (Or don't remember and come re-read this article whenever you need to. We'll be here!).
- Ensure you have updated all of your plugins and themes to the most recent version.
- If you have a caching plugin, ensure any caching is cleared to force all pages to be re-generated.
- Clear your browser cache and cookies. Click here for more information.
- Flush your CDN cache, if you are using a CDN, such as SiteLock.
- Log back into your WordPress dashboard.
These simple steps will resolve the vast majority of issues, as they will likely be caused by caching issues between the site before and after being updated. If this does not work, or if you are unable to perform these steps, continue to the more drastic options below:
- Disable ALL of your plugins: Any one of your plugins could cause your issue. You will need to disable all of them. If the issue is resolved, reactivate them one at a time until you identify the specific plugin that is not functional.
- Switch to the default WordPress theme: The following article will walk you through changing your WordPress theme to the most recent default:
- If you cannot switch themes: Use FTP to remove all theme folders except for the default theme you need to switch to, forcing it to load.
- Update WordPress manually: If all else fails, please attempt to update WordPress manually.
NOTE: Do not delete the wp-content directory or your wp-config.php file when following these directions.